In this blog post, we will understanding DNS servers, exploring its definition, purpose, functioning, types, and significance. So let’s start,
Understanding DNS Server: What it is and How it Works?
In today’s modern world, the internet is an integral part of our daily lives, providing us with a wide range of services such as communication, learning, shopping, and entertainment. However, have you ever stopped to think about how your device is able to access a website just by typing in its name? This is where the Domain Name System (DNS) server comes into play.
I. Understanding DNS Server
A. Definition: A DNS server is a vital component of the internet that translates domain names into IP addresses, enabling devices to connect to websites and other online resources.
B. Purpose: The primary function of a DNS server is to act as a directory service, allowing users to access websites and online services by using easy-to-remember domain names instead of complex IP addresses.
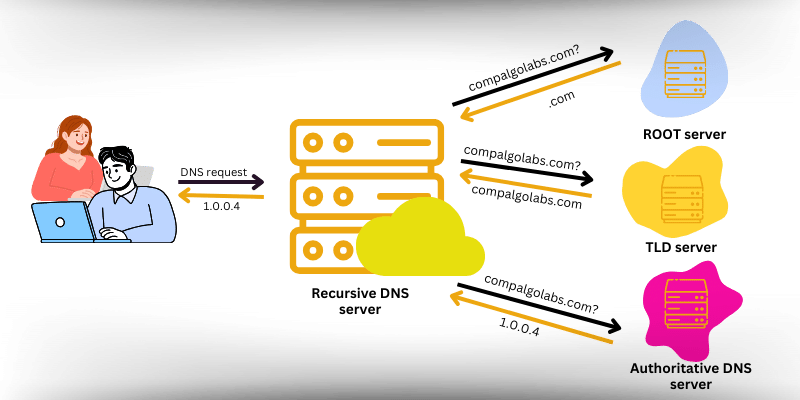
II. How It Works
A. Domain Names: Each website has a unique domain name (e.g. google.com) and an associated IP address (e.g. 8.8.8.8). The DNS server converts the domain name into an IP address, enabling your device to connect to the website’s server.
B. DNS Hierarchy and Resolution Process: The DNS system is structured hierarchically, with multiple levels such as the root, top-level domains (TLDs), and subdomains. When a domain name is entered, the DNS server undergoes a resolution process, starting from the root and moving down the hierarchy to find the corresponding IP address.
III. Different Types of DNS Servers
A. Primary DNS Server: The primary DNS server hosts the master copy of a domain’s DNS information and responds to queries for that particular domain.
B. Secondary DNS Server: Acting as a backup for the primary server, the secondary DNS server updates its DNS records from the primary server and responds to queries if the primary server is unavailable.
C. Caching DNS Server: This type of DNS server stores recently accessed DNS records, reducing the time taken to resolve a domain name and ultimately improving internet speed.
IV. Common DNS Server Issues
A. DNS Server Not Found/Error: This issue arises when the DNS server is unable to translate a domain name into an IP address, causing the website to be inaccessible.
B. DNS Cache Poisoning: A type of cyber attack where a hacker manipulates the cached DNS records, redirecting users to fake websites or phishing pages.
V. The Importance of DNS Servers
A. Accessibility: The existence of a DNS server eliminates the need for users to remember complicated IP addresses, making websites more accessible.
B. Security: DNS servers play a critical role in ensuring the security and authenticity of websites by verifying their IP addresses.
C. Speed: With the assistance of caching DNS servers, the time taken to resolve domain names is significantly reduced, resulting in faster internet speeds.
Conclusion :
In essence, the DNS server may appear insignificant in the grand scheme of the internet, yet it serves a crucial function in facilitating seamless connections between our devices and the online realm. Grasping its operations and various forms can help us recognize its significance and manage any potential challenges that may arise. Therefore, the next time we access a website, let us not forget the integral role that the DNS server plays in enabling this feat.
Can also read our other blogpost on topic The Crucial Role of Responsive Web Design in Capturing Global Audiences .




